MSDS is used in industries to know details in industry This blog is contains each term in details
Example: Dimethyl Ketone is also known as 2 - Propanone and in industry it is known as Acetone all nomenclature must be written.
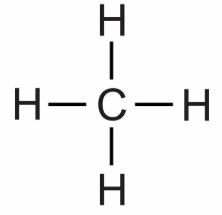
Example : Methane has following chemical structure
Read more about it - Click here
[ads id="ads1"]
TDG Flammability is a classification according their ability to Fire
Before we start
- MSDS full form Material Safety Data Sheet
- MSDS Indian standard has 10 Sections while international standard has 16 Sections.
- Content is same in both standards but International more classified example: Indian section 1 is divided in Section 1 & 2.
International Standard
|
Indian Standard
|
Section 1 :
Chemical Product & Company Identification
Section 2 :Composition
& Information on ingredients
Section 3 :Hazard
Identification
Section 4 :
First aid measures
Section 5 :Firefighting
measures
Section 6 :
Accidental release measures
Section 7 :Handling
& Storage
Section 8 :
Exposure control / Personal protection
Section 9 :Physical
& Chemical properties
Section 10 :Stability
& Reactivity
Section 11 :Toxicology
information
Section 12 :
Ecological information
Section 13 :Disposal
consideration
Section 14 :
Transport information
Section 15 :
Regulatory information
Section 16 :
Other information
|
Section 1 : Chemical Identity
Section 2 : Physical & Chemical data
Section 3 : Fire & Explosion data
Section 4 : Reactive data
Section 5 : Health hazard data
Section 6 : Preventive measures
Section 7 : Emergency & First aid measures
Section 8 :Additional information / references
Section 9 :Manufacturer / supplier’s data
Section 10 :Disclaimer
|
[ads id="ads1"]
Blog Content
MSDS Sections 1 to 10- Chemical Identity
- Physical & Chemical data
- Fire & explosion hazard data
- Reactivity data
- Health Hazard Data
- Preventive measures
- Emergency and first aid measures
- Additional information / References
- Manufacturer / Supplier data
- Disclaimer
Interview Questions from this blog
- What is CAS No, UN No, ADR No, Hazchem [EAC] No, Hazardous waste ID No ?
- What is LEL / UEL, TDG Flammability?
- What is TLV, STEL / SET, LC50 / LD50, Odour threshold NFPA Symbol?
- Which are routes of entry of chemical to enter in human body?
Section :1 - Chemical Identity
In this section- Name of Chemical
- Chemical Formula
- Synonyms
- Trade name
- Chemical Classification
- Regulated Identification
- Shipping Name, Code, Labels
- CAS No
- UN No
- ADR No
- Hazchem [EAC] No
- Hazardous waste ID No
- Hazardous Ingredients & CAS No
[ads id="ads1"]
Sec: 1 - 1. Name of Chemical
Chemical names as per all standards [like IUPAC] Common name, Alternate name, Industrial names include here.Example: Dimethyl Ketone is also known as 2 - Propanone and in industry it is known as Acetone all nomenclature must be written.
Sec: 1 - 2. Chemical Formula
It is symbolic presentation of any chemical of atoms.Example : Methane has following chemical structure
Sec: 1 - 3. Synonyms
Name or alternate of Chemicals must be included in this section.
Example :
Acetone has synonyms
- 2 - propanone
- beta - ketopropane
- dimethyl formaldehyde
- dimethyl ketone
- dimethylketal
- DMK (dimethyl ketone)
- keto propane
- methyl ketone
- pyroacetic acid
- pyroacetic ether
- Pyroacetic, spirit
Sec: 1 - 4. Trade name
Chemical have trade name must include in this section.
[ads id="ads1"]
[ads id="ads1"]
Sec: 1 - 5. Chemical Classification
It is general classification in terms- Organic or Inorganic
- Flammable
- Explosive
- Toxic
- Poisonous
- Corrosive
- Reactive
- Infectious
- Oxidizing
- Radioactive.
Sec: 1 - 6. Regulated Identification
- If any identification is provided by any regulatory body then it must be included in this section.
Sec: 1 - 7. Shipping name, Codes, Labels.
- Identification of material available for shipping then it must be included in this section.
Sec: 1 - 8. CAS Number.
- CAS No - Chemical abstract number
- It is unique identification number of chemical.
- Check CAS Numbers of Chemicals - Check here
Sec: 1 - 9. UN Number
- It is United nations four digit number.
- It is assigned to potential hazards of material.
- Example:
- Ammonia UN No : 1005
- This number is used by Emergency Response Person including Fire fighting persons.
- Read more for UN Numbers - Click here
Sec: 1 - 10. ADR Number
- ADR No - Agreement concerning carriage of Dangerous goods by Road.
- This is European agreement at Geneva by 19 Europe countries for chemical transportation by road.
- It is classifieds as below
- Class 1 : Explosive substances and articles.
- Class 2 : Gas - Compressed, Liquefied, or Dissolved under pressure
- Class 3: Flammable liquids.
- Class 4.1: Flammable solids
- Class 4.2: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion.
- Class 4.3: Substances which produces flammable gases.
- Class 5.1: Oxidizing substances.
- Class 5.2: Organic peroxide.
- Class 6.1: Toxic substances.
- Class 6.2: Repugnant substances and those who are infectious.
- Class 7 : Radioactive material.
- Class 8: Corrosive materials
- Class 9: Miscellaneous dangerous substances.
- Check more for ADR numbers - Click here
Sec: 1 - 11. Hazchem [EAC No] No
- Hazchem Code - Hazardous Chemical code
- EAC no - Emergency Action Code No.
- This code is conformed by Health & Safety Executive, UK.
- It is follow this sequence
- It has number 1 to 4.
- One or two letters.
- Fire extinguisher required.
- PPEs Required.
 |
| HAZCHEM Code |
- Example:
Sec: 1 - 12. Hazardous Waste ID No
- Waste ID is generated when material decomposition is required without heating.
- This is generated when material is reacted with basic environment like Water, Air, Soil etc
Sec: 1 - 13. Hazardous ingredients & It's CAS number
- If there is any Hazardous ingredient is used to produce material then its name & CAS Number is include in this section
[ads id="ads1"]
Section:2 - Physical & Chemical data
This section consists- Appearance, State & Odour
- Specific Gravity
- Vapour density
- Boiling point
- Melting / Freezing point
- Vapour pressure
- Solubility in water
- Scrubbing / Neutralizing / Inactive media.
- pH
- Others
Read more about it - Click here
[ads id="ads1"]
Section :3 - Fire & explosion hazard data
- Flash point
- Auto ignition temperature
- Flammable limits : LEL / UEL
- TDG Flammability
- Explosion sensitivity to impact
- Explosion sensitivity to static electricity
- Explosive material
- Flammable material
- Combustible and flammable material
- Pyrophoric material
- Hazardous combustible products
- Hazardous polymerization
- Corrosive material
- Organic peroxide
- Oxidizer
- Others
Sec-3 : 1. Flash point
- It is the temperature at which material gives vapour near its surface to form flammable mixture.
- This mixture caught fire when subjected to spark or Source of fire.
- Lower flash point of material is indicates high hazards of Chemical.
- It can be expressed in Closed cup CC & Open cup OC.
- Closed cup value is slight less than the Open Cup.
Sec-3 : 2. Auto ignition temperature
- It is the lowest temperature at which a material begins to burn in air without any contact of spark or flame.
- During heating if the material decomposes chemical may auto ignite at some temperature.
- This value is estimated due to it is derived from various methods.
- Material must be handled below auto ignition temperature.
Sec-3 : 3. Flammable limits : LEL / UEL
LEL - Lower Explosive Limit.- It is the minimum concentration of gas or vapour at which fire can placed with the help of spark or other fire source.
- It is the maximum concentration of gas or vapour above which fire can not be takes place.
- LEL and UEL closer for chemical safer it is.
- Chemical with lower LEL & Higher UEL is dangerous.
- Above UEL chemical is hazardous in open environment.
- Open environment is dilute gas or vapour of material and dilution can drop concentration below UEL.
- This dilution leads to fire.
- Unit of Concentration
- Gas or Vapour - % [1% = 10,000 ppm]
- Powder gm/m3
- Before any hot work Nitrogen flushing, LEL test & Oxygen test is carried.
- Flammable gas < LEL
- Oxygen < 0.5%
[ads id="ads1"]
Sec-3 : 4. TDG Flammability
TDG - Transportation of Dangerous GoodsTDG Flammability is a classification according their ability to Fire
- 2.1 Flammable Gas
- 3 Flammable liquids
- 4.1 Flammable solids
- 4.2 Spontaneous combustible material.
- 4.3 Material which gives off a flammable gas on contact with water.
Sec-3 : 5. Explosion sensitivity to impact
- If any material caught fire on impact shock friction or drift data must be included here.
Sec-3 : 6. Explosion sensitivity to static electricity
- Chemical Gas or vapour which can ignite on static electricity or electric spark, data must mention here.
Sec-3 : 7. Explosive material
- Schedule - 1 of Manufacturing, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules, 1989 defines EXPLOSIVES.
- Explosives are those materials which explode under effect of flame, heat, or photo chemical conditions.
- Chemicals which are more sensitive to shocks or friction than dinitrobenzene [old definitions] or Pyrotechnic substances [Fire works].
- Substances which is capable of producing gas at such Temperature or Pressure and Speed to cause damage to surroundings or exothermic reaction reaction by heat, light, sound, gas, smoke, or their combination [New definitions].
Sec-3 : 8. Flammable material
Under MSIHC Rules data must include in this section- Flammable gases with LEL up to 13% explosive range
- Extreme flammable liquids with Flash point < 23℃ Boiling point < 35℃
- Very highly flammable liquid with flash point < 23℃ Boiling point > 35℃
- Highly flammable liquid with flash point 23℃ - 60℃
- flammable liquid with flash point 60℃ - 90℃
Sec-3 : 10. Pyrophoric material
- Definition : Any material that can ignite on the spot in air at 54.4℃
- Example :
- Solids - Titanium dichloride and phosphorous.
- Liquid - Tributyaluminium and its related compounds.
Sec -3 : 11. Hazardous combustible products
When Product burns and produces hazardous products must include in this sectionSec -3 : 12. Corrosive material
- Any material which is able to corrode / damage human tissue
- Which is capable to weak vessel or container called Corrosive material.
Sec-3 : 13 Hazardous polymerization
- Polymer is a natural or man-made material formed by combining units called monomer.
- Uncontrolled polymerization can be hazardous.
- Polymerization may exothermic process, rapidly increase temperature or pressure.
- Inhibitors [Negative Catalyst] are added to slow the process.
Sec-3 :14. Organic peroxide
- Peroxide release atomic [nascent] oxygen rapidly.
- Peroxides poses fire hazard in contact with combustible materials.
- Peroxides are used as
- Oxidizing agents
- Bleaching agents
- Polymerization initiators.
- Organic peroxides contain bivalent 0-0 structure,are thermally unstable.
- They are exothermic and undergo rapid self accelerating decomposition.
Sec-3 :15 Oxidizer
- Oxidizer - Compounds which are spontaneously release oxygen at room temperature or slight heating.
- It reacts strongly at high temperature.
- It is violent with cellulose, Organic compound and reducing agent.
- Oxidizers are
- Peroxides
- Perchlorate
- Chlorates
- Nitrites
- Permanganates
- Storage area must be ventilated and cooled
- Chemicals with this properties must included here
Sec-3 : 16. Other hazardous properties available then it must included here
[ads id="ads1"]
Section: 4 - Reactivity data
This section include following data- Chemical Stability
- Incompatibility
- Reactivity
- Hazardous reaction products.
Sec-4 : 1. Chemical Stability
- Stable compound does not easily decompose or react readily.
- Stable compounds are remains unchanged in the presence of of heat, moisture or air.
- Unstable compound may decompose, polymerize, burn, explode,under normal environmental conditions. Special environment is required to store this compounds.
- Examples:
- CS2 decomposes in light and burns due to heat, spark, or friction, it relese SOx when burn.
- Caprolectum liberates NOx when heated.
- TNT explodes when shock applied.
Sec-4 : 2. Material incompatibility.
- Incompatibility of material - Disability to co- exists permanently together.
- Example :
- Water and alcohol can co exist together for long period.
- Toluene reacts violently with some acids, plastics, or rubber.
- Incompatible materials can cause fire, explosion, toxic releases, polymerization or destroy the structure or function disability.
Sec-4 : 3. Reactivity
- Two or more chemicals can react with each other and gives react products.
- 2H2 + O2 --. 2H2O
- In this section if any chemical is violent reaction with easily available chemicals air, or water data must include here.
- Storage, handling and reactivity data include in this section.
- Example:
- Sodium metal rapidly react with water.
- Phosphorous reacts rapidly in air.
Sec-4 : 4. Hazardous reaction products.
- Hazards related to reaction like poisonous, explosive, exothermic included here.
- Example:
- When Chlorine react with Alcohol it produces explosive alkyal hypochlorite.
- If any toxic gas release during reaction scrubbing media must be included in this section.
[ads id="ads1"]
Section 5 : Health Hazard Data
This section is most important content is- TLV
- STEL / SET
- LC50 / LD50
- Odour threshold
- Carcinogen / Poisonous
- Routes of Entry.
- Body parts that may affected.
- Effects of exposure and symptoms.
- Emergency & First aid treatment.
- Engineering controls necessary for safe handling
- NFPA Hazard signals
- Special Health hazards.
Sec-5 : 1. TLV
TLV - Threshold Limit Value.- This term is prepared by ACGIH
- TLV is advisory limit it is not rule enforced limits.
- TLV is sub divided in 3 sections
- TWA - Time weight average.
- STEL - Short Term Exposure Limit
- CEL - Celling Exposure Limit
TWA - Time weight average.
- If chlorine include in your process the its TWA is 0.5 ppm.
- Upto 0.5 ppm employees can work safely without any health chronic or adverse effect.
- Chlorine's STEL is 2PPM
- Worker is working in this concentration then it must follow this guideline
- He can work for 15 minutes
- 15 minutes working cycle can be carried for 4 times only.
- After each 15 minutes working cycle person will take rest of 2 hours
It is maximum exposure limit that must not exceed at any part of work day.
Sec-5 : 3. LC50 / LD50
LC50 - Lethal concentrationLD50 - Lethal dose
- LC50 is air volume concentration ppm at which 50% persons will die due to inhalation.
- LD50 Is weight concentration mg/kg on which oral or lethal dose single exposure 50% person will die
Sec-5 : 4. Odour threshold
It is the lowest concentration in ppm which can smell by human being.This limit must be include here.
Sec-5 : 5. Carcinogenic / Mutagenic / Teratogenic / Poisonous
- Carcinogenic
- Chemicals which are boosting cancer called Carcinogenic.
- Mutagenic
- Chemicals which are effecting DNA of human being is called Mutagenic
- Teratogenic
- Chemicals which are affecting fertility of human being is called Teratogenic chemical
- Poisonous
- Chemical which are capable to cause death or illness.
Sec-5 : 6. Routes of Entry.
- Absorption through skin - Dermal tract.
- Ingestation from mouth - Digestive tract.
- Inhalation from air - Respiratory tract.
- Organic solvents are easily absorb through skin.
- Nitro-benzene, Aniline, Phenol, Nicotine is penetrate up to blood stream.
- Full sleeve shirt can protect a while.
It happen due to -
- Diry Dishes & Glass used in plant.
- Contaminated food, Water in plant.
- Eating food or drinking water, beverages without washing hands.
- Eating Pan Supari, Tobacco, Lime in plant without washing hands.
Chemicals enter in human body mostly with this path. It happen due to
- Volatile materials used without scrubbing unit, Loose connections / flanges.
- Open Vessels, Drums or containers leads to this
- Some of vapour or gas is trapped by mucus, scavenger cells, lungs and deposit on various tissues or organs.
- Proper maintenance in connection piping, Enclosed vessels, Well ventilation, Good housekeeping on spillage PPEs can improve environment.
Sec-5 : 7. & 8. If any Body parts that may affected & Effects of exposure and symptoms found it must include in this section.
Sec-5 : 9. NFPA Symbol
- NFPA symbol is developed by NFPA - National Fire & Safety Protection Association America.
- This is NFPA Symbol contains 4 diamonds with 0 to 4 number.
- Red - Fire potentiality :
- 0 : Material will not burn
- 1 : Combustible if heated [Flash point > 200℉]
- 2 : Caution - Must be heated or exposed to higher temperature to ignite [Flash point < 200℉]
- 3 : Warning - Can be ignited under most ambient temperature conditions.
- 4 : Danger - Chemical will rapidly vaporize or disperse in air at ambient conditions and burn readily [Flammable gases and highly flammable liquids ; Flash point < 73℉]
- Blue - Health Hazard :
- 0 : No Unusual hazard
- 1 : Caution - May cause irritation
- 2 : Warning - May be harmful if inhaled or absorbed.
- 3 : Hazardous - Corrosive or Toxic if inhaled or absorbed can cause serious injury
- 4 : Deadly - May be fatal upon even short term exposure
- Yellow - Reactivity :
- 0 : Normally stable, Water reactive.
- 1 : Caution - May react mildly if heated or mixed with water.
- 2 : Warning - Unstable, May react violently with water.
- 3 : Hazardous - May react explosively if shocked, under confinement, Heated under.
- 4 : Danger - May detonate or explode at ambient conditions.
- White - Special hazard :
Sec-5 : 10. Special Health hazards data is available must include here
[ads id="ads1"]
Section :6 - Preventive measures
- Ventilation required and type
- Personal protective equipments required and type.
- Handling and storage precaution.
Sec-6 : 1. Ventilation required and type
- Ventilation is required to provide fresh air.
- Ventilation is selected as per rate of heat generation, Gas vapour dust generation.
- Types of ventilation
- Natural Ventilation
- Dilution or cross ventilation
- Roofed ventilation.
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Building ventilation
- Process ventilation
- Air distribution
- Air Conditioning
- Special Ventilation
- Open surface tanks
- Spray booths
- Foundries
- Grinding buffing and polishing
- Wood working
- Cast iron machining
Read more in detailed - Click here.
Sec-6 : 2. Personal protective equipments required and type.
Personal protection equipments, PPEs required for handling & processing must include hereRead more in detailed - Click here.
Sec-6 : 3. Handling and storage precaution.
Handling and storage data included in this section- Special storage requirements
- List of compounds from which to be separated
Section : 7 Emergency and first aid measures
In this section following data must be included- Steps to be taken in the case of or spillage or leakage
- Waste disposal method for solid, liquid or gas waste
- Fire, extinguishing media, special procedures if available and Unusual hazards.
- Exposure - First aid measures, antidotes, doses etc.
Section : 8 - Additional information / References
If any data or references available include in this section
Section : 9 - Manufacturer / Supplier data
Following data of manufacturer / supply in MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet
- Name of firm
- Mailing address
- Contact / Telephone number / Telex / Fax nos
- Contact person in emergency
- Local bodies involved
- Standard packing
- Tremcard details
- Other
Section : 10 - Disclaimer
[ads id="ads1"]
Legal disclaimer included in this section
Watch Industrial Guide MSDS Video -
Read more about "Safety" from Industrial Guide - Click here
Important linksWikipedia - Read now
Handling & storage guide line in PDF - Download Now
Responsibility about MSDS Uregics - Check now
Download MSDS
MSDS - Check now