This blog contains following topics study
- Fire definition
- Fire Pyramid ( Fire Triangle + One morden concept element)
- Fire extinguishing
- Stages of Fire & Dire detectors
- Reasons of fire
Fire definition
Fire is a rapid redox reaction which is accompanied by Heat, Smoke and flame.
Fire Pyramid
Three elements are necessary to iginite fire and Fourth element to continue it.
1. Fuel
2. Oxygen or Oxydiser
3. Heat or Source of fire
4. Chain reaction in fire which continues fire.
Incomplete Fire produces carbon monoxide which is toxic and creates invisibility which can affect fire extinguishing team.
[ads id="ads1"]
Stages of Fire and Fire Detectors
1. Incipient Stage
The incipient stage is the initial stage of fire where combustion begins at a molecular level.
- Ionization of air particles occurs
- No visible flame or smoke
- Heat generation is very low
Suitable Detector:
- Ionization Smoke Detector – Detects invisible combustion particles at an early stage
2. Smoldering Stage
This stage involves slow combustion without open flames.
- Visible smoke is generated
- Heat increases gradually
- Fire can remain unnoticed for a long time
Suitable Detectors:
- Ionization Smoke Detector
- Photoelectric Smoke Detector
- Aspirating Smoke Detection System (VESDA)
3. Flame Stage
In this stage, open flames start to appear.
- Flames become visible
- Smoke reduces
- Heat increases rapidly
Suitable Detectors:
- Flame Detectors
- Infrared (IR)
- Ultraviolet (UV)
- UV/IR Combination
4. Heat Stage
This is the fully developed fire stage.
- High temperature
- Flame, smoke, and fire gases present
- Severe damage potential
Suitable Detectors:
- Heat Detectors
- Fixed Temperature Detector
- Rate-of-Rise Detector
Key Points
- Early fire detection minimizes damage and downtime
- Correct detector selection depends on the fire stage
- Combination of detectors improves fire protection effectiveness
Fire extinguishing
Fire can be stopped by remove one element
1. Starvation: Stop or remove fuel.
2. Smothering: Remove oxygen below 14 ~ 18% by adding inert gas like CO2 or Nitrogen
3. Cooling: Remove heat faster than libration. Effective in stationary fire.
4. Chain Reaction Inhibition: Break chain reaction by removing free redicals in fire.
5. Dilution: Fire in Gases can be extinguished by reduction concentrarion of Fuel by adding Inert Gases/ Steam.
Effective in small fire and Confined space
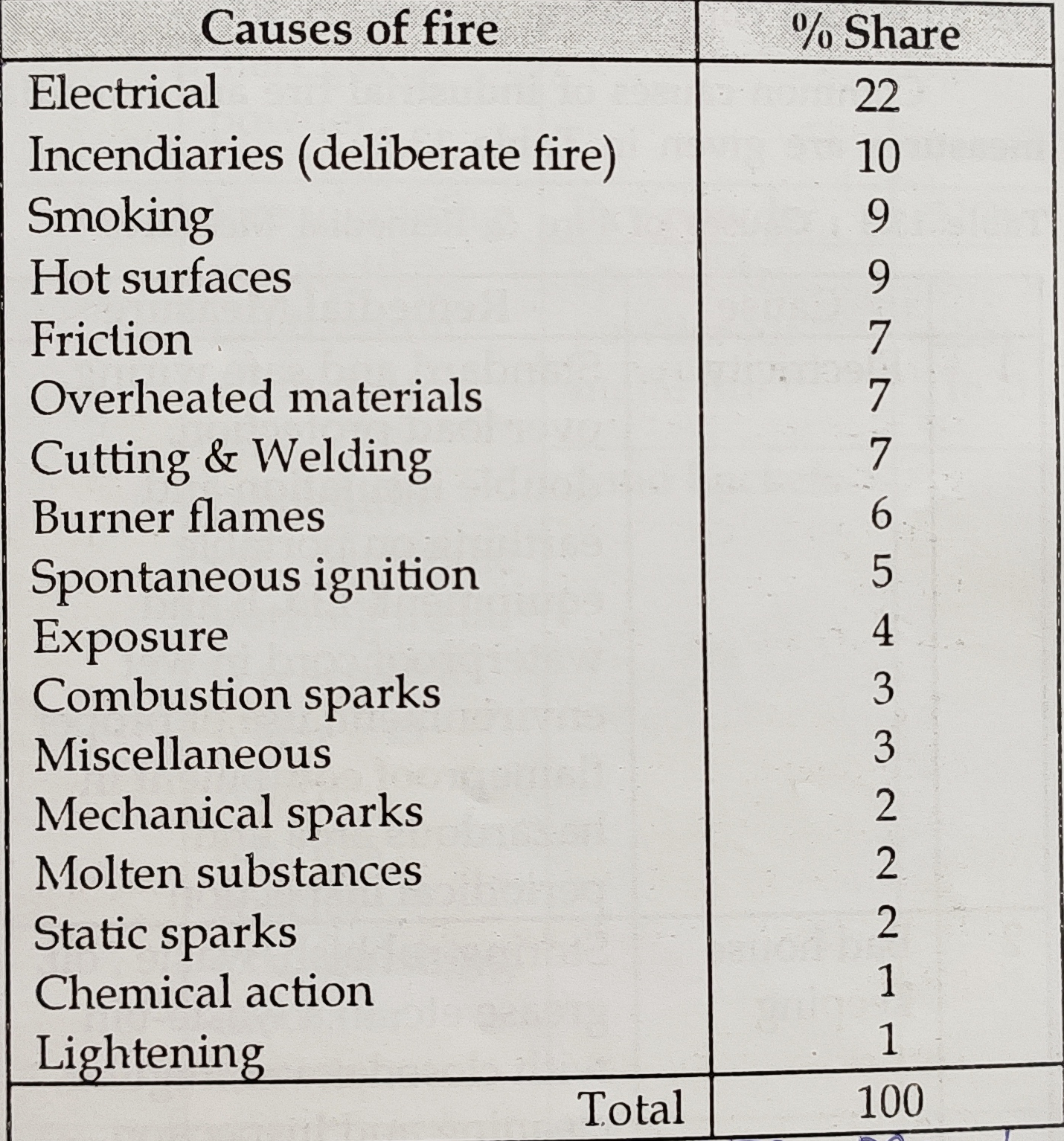
Reasons of fire
Why Fire Happens in Industries – Major Reasons of Industrial Fires
1. Presence of Flammable Materials:
Industrial fires occur due to flammable gases, liquids, vapors, and combustible dust commonly used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries.
2. Leakage and Spillage of Chemicals:
Fires start when flammable substances leak or spill because of corrosion, poor storage practices, gasket failure, or equipment malfunction.
3. Ignition Sources in Industrial Areas:
Hot work such as welding, cutting, grinding, electrical sparks, open flames, and hot surfaces are frequent ignition sources of industrial fires.
4. Electrical Fire Causes:
Short circuits, overloaded cables, loose connections, damaged insulation, and improper earthing are leading causes of electrical fires in industries.
5. Static Electricity Hazards:
Static charge generated during transfer, filling, or mixing of flammable liquids can ignite vapors if grounding and bonding are inadequate.
6. Mechanical Equipment Failure:
Overheating of pumps, motors, bearings, and friction between moving parts can generate heat sufficient to ignite flammable materials.
7. Process Upsets and Abnormal Conditions:
High temperature, high pressure, runaway chemical reactions, or loss of cooling systems can lead to fires in process industries.
8. Human Error and Unsafe Practices:
Surveys indicate that nearly 50% of industrial fires are caused by human error, including unsafe work practices, bypassing safety systems, and lack of training.
9. Poor Housekeeping:
Accumulation of combustible waste, oil-soaked rags, chemical residues, and dust significantly increases the risk of industrial fires.
10. Inadequate Fire Protection Systems:
Failure or absence of fire detection, alarm, suppression systems, and poor preventive maintenance allow small fires to escalate into major incidents.
These are the primary reasons why fires occur in industries, highlighting the importance of fire prevention, process safety, and effective fire protection systems.
Study of 25000 reported cases from 1968 to 1977 by Government of India