HAZOP- HAZard and OPerability Study is a systematic and structured technique commonly used in identifying potential hazards and/or problems with plant operability, recognizing consequences arising from various causes and providing recommendations for safety improvements in design and operations.
It is an important industrial Safety tool.
Carried out during the design stage of plant or during carrying out any modification in existing plant.
Team Members
If HAZOP is carried out for existing plant , Team normally consists of members from relevant fields mainly process engineer, Safety engineer, mechanical engineer , chemist and operation engineer and independent team leader or chairman.
If Hazard is carried out for new design plant then Design engineer, process engineer and commissioning engineer along with team as mentioned above.
Requirements for HAZOP
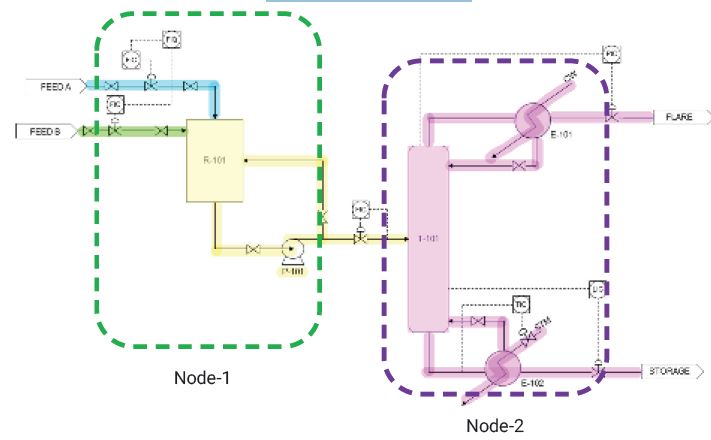
- Process flow diagrams, along with heat and material balances
- Process descriptions with interlocks descriptions
- Piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs)
- Equipment layout drawings
- Unit plot plans
- Material safety data sheets (MSDS) for hazardous chemicals
- Equipment and instrument datasheets
- Project control philosophy and cause-and-effect diagrams
- Provisional operating instructions, and startup and emergency shutdown procedures
- Utility specifications (as applicable).
How HAZOP is carried out?
Since the nature of operations for continuous processes and batch processes are different, it is important to use a different set of guide words for these processes.
A deviation can be defined as process conditions departing from their intention. A deviation is a combination of “guide word” and “process parameter.”
Guideword is a short word to define a deviation from the intention (e.g. , more, less, no, reverse, other than). A process parameter is a relevant parameter for the conditions of the process (e.g., pressure, temperature, flowrate, composition, etc.)
Generally used Guide Words are:-
- No
- More
- Less
- As Well As
- Part of
- Reverse Other than
- Input streams to the equipment
- Output streams from the equipment
- Utility connections to/from the equipment
- Vent lines, drain lines, overflow lines
- Equipment, such as a reactor, tank, heat exchanger, dryer, centrifuge, etc.
- Each node from each input/output stream should be marked in the P&ID, preferably with different color codes. These nodes are normally identified by a HAZOP study team leader, with assistance from the process engineer, well before the HAZOP study session.
- Long nodes running into two or more P&IDs, consisting of a number of lines and equipment within the same node, are sometimes identified by team leaders. This should be avoided, as a HAZOP study is likely to miss some probable causes and consequences, decreasing the study’s overall effectiveness.